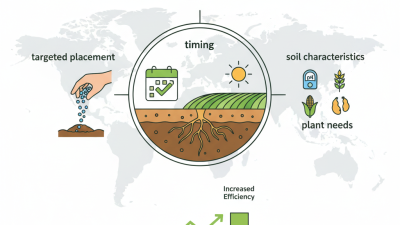
Water Soluble Magnesium Fertilizer plays a crucial role in modern agriculture. Magnesium is vital for plant processes such as photosynthesis and nutrient uptake. According to industry reports, about 50% of crops may show magnesium deficiency. This can lead to decreased yield and quality.
Incorporating Water Soluble Magnesium Fertilizer into crop management can boost overall plant health. Research shows that magnesium enhances chlorophyll production, improving growth and resilience. However, over-application can lead to toxicities. This prompts the need for precise application strategies based on soil and crop needs.
Understanding how to utilize Water Soluble Magnesium Fertilizer effectively is essential. Balancing magnesium levels is key to promoting optimal plant development. While many farmers recognize magnesium's importance, some still overlook tailored application methods. This highlights a gap in knowledge that requires attention for improved agricultural practices.

Water soluble magnesium fertilizer offers essential benefits for plant growth. Magnesium is a vital nutrient that enhances chlorophyll production. This process boosts photosynthesis, improving overall plant health. When plants lack magnesium, they may show signs of yellowing leaves and stunted growth. Using this type of fertilizer can prevent these issues effectively.
Here are some tips for using water soluble magnesium fertilizer. Always test your soil before application. This helps determine magnesium levels. Overuse can harm plants. Mix the fertilizer with clean water according to the package instructions. Applying it during the growing season maximizes its effectiveness. Consider using a sprayer for even distribution.
Remember that not all plants require the same amount of magnesium. Some may thrive with minimal amounts, while others might need more. Observing your plants can help you adjust the dosage over time. Keep an eye on their progress and adjust accordingly. Finding the right balance takes time and practice. Don't hesitate to experiment with small batches first. This will help you understand what works best for your garden.
When considering water-soluble magnesium fertilizers, it's essential to identify suitable crops that can benefit the most. Research indicates that leafy greens, such as spinach and lettuce, have shown significant yield increases with proper magnesium application. According to a recent study by the American Society of Agronomy, magnesium deficiencies can reduce photosynthesis by over 30%. This makes magnesium crucial for crops that require dense foliage.
Tomatoes and peppers also thrive with magnesium. A report from the International Plant Nutrition Institute highlighted that magnesium improves fruit quality and size in these crops. These plants need magnesium for enzyme activation and chlorophyll production. Interestingly, applying water-soluble magnesium during early growth stages can enhance nutrient absorption and minimize deficiency risks.
Tips: Always test soil for magnesium levels before application. This ensures that you provide the right amount. Over-application can lead to nutrient imbalance. Monitor your crops closely, as signs of magnesium deficiency can include yellowing leaves. Regular assessments allow for timely adjustments in fertilizer use, promoting healthier plants.
Water soluble magnesium fertilizer is essential for many crops. It improves plant health and boosts yield. However, proper application techniques are crucial for effectiveness. Research shows that magnesium deficiency can lower crop yields by up to 30%. Thus, using the right methods for application is key.
One effective technique is foliar application. Mixing the fertilizer with water allows for quick absorption. It’s recommended to apply it early in the morning or late in the afternoon. The cooler temperatures help prevent evaporation and enhance uptake. Avoiding high temperatures is critical, as it can cause leaf burn. Another method is soil application. This involves dissolving the fertilizer in irrigation water. Studies reveal that magnesium is most effective when the soil pH is around 6.5. This pH level optimizes nutrient availability.
Nevertheless, over-application can lead to imbalances. Excess magnesium can inhibit the uptake of calcium and potassium. Farmers should monitor soil and plant tissue regularly. Testing can prevent potential issues. Careful planning and assessment are vital in maximizing magnesium fertilizer's benefits while minimizing drawbacks.
| Application Method | Recommended Concentration | Best Time of Application | Crop Type | Frequency of Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foliar Spray | 0.2% - 0.5% | Early Morning or Late Afternoon | Vegetables | Every 2-4 weeks |
| Drip Irrigation | 0.1% - 0.3% | During Irrigation Cycles | Fruit Trees | Every 3-4 weeks |
| Soil Application | 1-2 kg/ha | Before Planting | Cereals | Once per season |
| fertigation | 0.2% - 0.4% | At Key Growth Stages | Flowers | Once per 2-3 weeks |

When using water-soluble magnesium fertilizer, determining the right dosage is crucial. Research shows that magnesium is vital for plant growth. In fact, a study by the International Journal of Plant Sciences indicates that magnesium deficiency can reduce crop yields by up to 30%. This highlights the importance of providing adequate magnesium levels.
The recommended dosage for most crops ranges from 10 to 30 grams per square meter. However, this can vary based on soil conditions. For instance, sandy soils may require higher doses due to lower nutrient retention. It’s important to regularly test soil magnesium levels. This could prevent potential over-fertilization, which can harm plants. Striking a balance is vital.
Frequency of application also matters. Applying magnesium fertilizer every four to six weeks can help maintain optimal levels during the growing season. However, over-application can lead to nutrient imbalances. Observing plant health is essential. If leaf margins burn or discoloration occurs, rethink your approach. Efficient use of magnesium fertilizer involves monitoring, adjustment, and sometimes, trial and error.
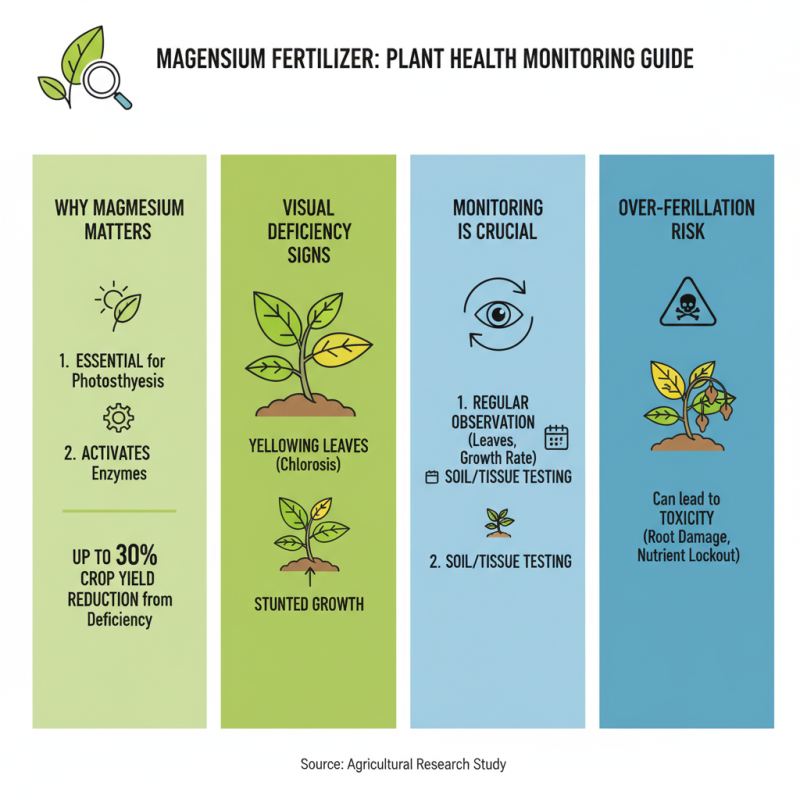
Monitoring plant health is crucial when using water-soluble magnesium fertilizer. Magnesium plays a vital role in photosynthesis and enzyme function. A study indicated that magnesium deficiency can reduce crop yield by up to 30%. This statistic emphasizes the importance of regular monitoring. Visual signs like yellowing leaves or stunted growth may indicate magnesium deficiency. However, over-fertilization can lead to toxicity.
Soil tests should be routine. They help determine magnesium levels and inform fertilization strategies. The ideal magnesium concentration in soil is around 50-100 mg/kg. If levels dip below this range, adjustments are necessary. Farmers often overlook the impact of soil pH on magnesium availability. A pH of 6.0-7.0 optimizes nutrient uptake.
By observing plant cues and conducting regular soil tests, growers can refine their magnesium application strategies. Keep in mind that every environment is unique. What works for one field might not work for another. Continuous reflection on results is vital. Adaptation is key. Each season offers new data to enhance future practices.