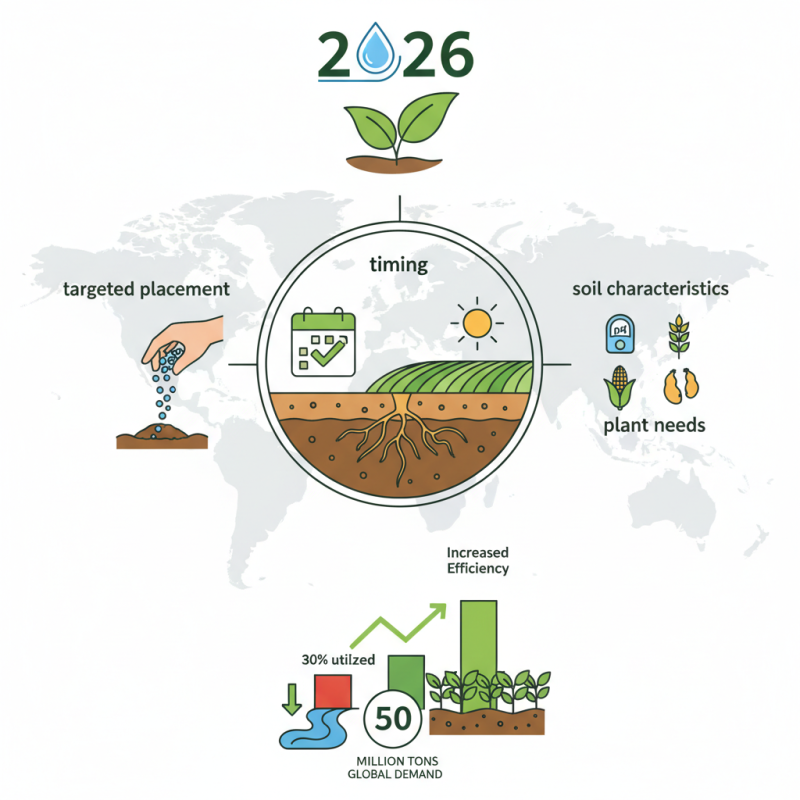
Water Soluble Phosphatic Fertilizers play a crucial role in modern agriculture. According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization, the global demand for phosphorus fertilizers is expected to reach 50 million tons by 2026. This increase highlights the necessity for farmers to adopt efficient methods of using these fertilizers.
Efficient utilization of Water Soluble Phosphatic Fertilizers can significantly boost crop yields. However, misapplication can lead to nutrient runoff and environmental issues. Research shows that only about 30% of applied phosphorus is effectively utilized by plants. This raises concerns about sustainable farming practices and necessitates a re-evaluation of current methods.
Farmers need to reflect on their fertilization strategies to ensure better nutrient absorption. Innovative application methods, such as targeted placement and timing, can enhance the efficiency of Water Soluble Phosphatic Fertilizers. Understanding soil characteristics and plant needs is essential for optimal results.
Water soluble phosphatic fertilizers are essential for enhancing plant growth. They provide phosphorus in a form that is readily available for absorption. Phosphorus plays a crucial role in energy transfer and photosynthesis. Using these fertilizers can lead to more robust root systems and better flowering.
To use water soluble phosphatic fertilizers effectively, it’s important to pay attention to application rates. Over-fertilization can harm plants and pollute waterways. Diluting the fertilizer properly is key. For instance, a common practice is to mix it with irrigation water. This method ensures that nutrients are delivered directly to the roots. However, monitoring the plants' response is necessary.
While the benefits are clear, challenges exist. Some growers may struggle with soil pH levels. An incorrect pH can hinder phosphorus availability. Regular soil testing can help address this issue. It's crucial to adapt strategies based on specific conditions. This approach ensures optimal nutrient uptake and plant health. Thus, careful management and observation are vital for achieving desired results.
Choosing the right type of water soluble phosphatic fertilizer is crucial for maximizing crop yield. Different crops have varying nutrient needs. For example, leafy greens may require higher phosphorus levels for robust growth. In contrast, root vegetables benefit from balanced nutrition. You must match fertilizer types to your specific crop requirements.
Consider the nutrient composition. Some fertilizers provide a higher percentage of phosphorus. Others include micro-nutrients like zinc or manganese. While this can enhance soil health, too much of a good thing can lead to nutrient imbalances. It’s essential to conduct soil tests before application. These tests reveal the existing nutrient levels and guide your fertilizer selection.
The timing of application is another factor. Some fertilizers perform better when used during specific growth stages. Early application might promote strong root systems, while later use supports flowering and fruit development. However, miscalculating the timing can prove damaging, leading to nutrient runoff or plant stress. It's a learning process. Each crop cycle offers insights into what works best in your unique conditions.
Water soluble phosphatic fertilizers are crucial for boosting plant growth. Choosing the right application method ensures these nutrients reach your plants effectively. One popular technique is fertigation, where fertilizers mix with irrigation water. This method delivers nutrients directly to the roots. Adjusting the pH of the solution can enhance nutrient absorption.
Spraying diluted fertilizers on the leaves can also work wonders. Leaf applications allow quick nutrient uptake, especially during critical growth stages. However, one must be cautious about the concentration. Overdoing it can lead to leaf burn. Testing a small area first is wise.
Tips for success: Always follow the recommended dosage. More does not mean better. Monitor your plants regularly for signs of deficiency or excess. Remember, balance is key in fertilization. Adjust your methods based on the crop's needs and local soil conditions. Experimenting might show that what works in one season does not work in another. Stay observant and be ready to adapt.

Timing is crucial when applying water-soluble phosphatic fertilizers. Ideally, applications should align with the plant's growth stages. When plants are actively growing, they absorb nutrients more efficiently. Early spring, before the main growing season, is an excellent time for application. It gives plants a head start.
Frequency matters, too. Over-fertilizing can harm plants. Aim for smaller doses more often. For many plants, a bi-weekly application during peak growth can enhance results. Observe your plants; their growth can guide you. If they look unhealthy, consider adjusting your schedule.
You may face challenges while applying these fertilizers. Soil moisture and temperature can affect nutrient uptake. Ensuring even distribution is tough but necessary. Sometimes, results may not meet expectations. Reflecting on these experiences can lead to better practices in the future. Adjustments based on actual observations help in optimizing fertilizer use.
When using water-soluble phosphatic fertilizers, monitoring nutrient uptake is crucial. Regular soil tests help identify nutrient levels. Farmers should test soil before and after fertilizer application. Soil health depends on the right balance of nutrients. Over-fertilization can lead to nutrient runoff, harming nearby ecosystems. It’s essential to apply the correct amount based on specific crop needs.
Adjusting fertilizer practices based on plant response is key. Observe crop growth and color changes. Yellowing leaves may indicate nutrient deficiencies. However, a sudden green-up could signal over-fertilization. Regularly checking moisture levels can prevent leaching and ensure consistent nutrient availability. These observations guide farmers in making timely adjustments.
It’s important to note that soil conditions vary. Each field may react differently to fertilizers. What worked last season may not apply this year. Learning from previous experiences helps refine practices. Engaging with local agricultural experts can provide insights. This collaborative approach encourages better soil health and maximizes crop yields.
| Crop Type | Recommended Dosage (kg/ha) | Application Timing | Nutrient Uptake (%) | Soil pH Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | 50 | Pre-plant and at Flowering | 30 | 6.0 - 7.0 |
| Corn | 80 | At Planting and V6 Stage | 40 | 5.5 - 6.8 |
| Wheat | 60 | Pre-plant and Boot Stage | 35 | 6.0 - 7.3 |
| Soybeans | 70 | Planting and Early Flowering | 25 | 6.0 - 7.5 |






